Wireless On-Off Switch:
Small and simple circuit, Suitable for home appliances
Normally home appliances are controlled by means of switches, sensors, etc. However, physical contact with switches may be dangerous if there is any shorting. The circuit described here requires no physical contact for operating the appliance. You just need to move your hand between the infrared LED (D2) and the photo-transistor (Q1). The infrared rays transmitted by D2 is detected by the photo-transistor to activate the hidden lock, flush system, hand dryer or else. This circuit is very stable and sensitive compared to other AC appliance control circuits. It is simple, compact and cheap. Current consumption is low in milliamperes. The circuit is built around an IC CA3140, D2, photo-transistor and other discrete components.
Parts:
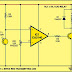
R1 = 470R
R2 = 100K
R3 = 3.3K
R4 = 10K
D1 = 1N4007
D2 = IR LED
Q1 = L14F1
RL = 5Vdc Relay
IC = CA3140
Q2 = BC548
Circuit Operation:
When regulated 5V is connected to the circuit, D2 emits infrared rays, which are received by photo-transistor Q1 if it is properly aligned. The collector of Q1 is connected to non-inverting pin 3 of IC1. Inverting pin 2 of IC1 is connected to voltage-divider preset R4. Using preset R4 you can vary the reference voltage at pin 2, which also affects sensitivity of the photo-transistor Op-amp IC1 amplifies the signal received from the photo-transistor Resistor R3 controls the base current of transistor BC548 (Q2). The high output of IC1 at pin 6 drives transistor Q2 to energies relay RL1 and switch on the appliance, say, hand dryer, through the relay contacts. The working of the circuit is simple. In order to switch on the appliance, you simply interrupt the infrared rays falling on the photo-transistor through your hand. During the interruption, the appliance remains on through the relay. When you remove your hand from the infrared beam, the appliance turns off through the relay. Assemble the circuit on any general-purpose PCB. Identify the resistors through colour coding or using the multimeter. Check the polarity and pin configuration of the IC and mount it using base. After soldering the circuit, connect +5V supply to the circuit.














0 comments:
Post a Comment