REMOTE CONTROLS are used everywhere these days. It’s making life of us simpler.Wireless communication is the transfer of information between two or more points that are not connected by an electrical conductor.The most common wireless technologies use electromagnetic wireless telecommunications, such as radio. With radio waves distances can be short, such as a few meters for television remote control, or as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mice, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones.
INTRODUCTION:
A remote control is a component of an electronics device, most commonly a television set, DVD player and home theater systems originally used for operating the device wirelessly from a short line-of-sight distance. Remote control has continually evolved and advanced over recent years to include Bluetooth connectivity, motion sensor enabled capabilities and voice control.Commonly, remote controls are Consumer IR devices used to issue commands from a distance to televisions or other consumer electronics such as stereo systems, DVD players and dimmers. Remote controls for these devices are usually small wireless handheld objects with an array of buttons for adjusting various settings such as television channel, track number, and volume. In fact, for the majority of modern devices with this kind of control, the remote control contains all the function controls while the controlled device itself has only a handful of essential primary controls. Most of these remote controls communicate to their respective devices via infrared signals and a few via radio signals. Earlier remote controls in the 1970s used ultrasonic tones. The remote control code, and thus the required remote control device, is usually specific to a product line, but there are universal remotes, which emulate the remote control made for most major brand devices.The main technology used in home remote controls is infrared (IR) light. The signal between a remote control handset and the device it controls consists of pulses of infrared light, which is invisible to the human eye.TERMINOLOGY USED :
1.Infrared: Infrared (IR) light is electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than those of visible light, extending from the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum at 700 nanometers (nm) to 1 mm .2. Sensor: A sensor (also called detector) is a converter that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an (today mostly electronic) instrument3. Receiver: receiver is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form.MATERIALS USED:
Ø TSOP 1738Ø 4 capacitors (100uF , 1uF ,.1uF , 1000uF)Ø transistor (BC 557)Ø 6 resistors(330ohm ,10k, 1k,1k)Ø IC 7805Ø 2 LED (BLUE,RED)Ø 9V BATTERY.Transistor BC557:BC 557 is a small, common PNP BJT transistor used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications.FEATURES•Low current (max. 100 mA)•Low voltage (max. 65 V).APPLICATIONS•General purpose switching and amplification.DESCRIPTIONPNP transistor in a TO-92; SOT54 plastic packageTSOP 1738The TSOP 1738 is a member of IR remote control receiver series. This IR sensor module consists of a PIN diode and a pre amplifier which are embedded into a single package. The output of TSOP is active low and it gives +5V in off state. When IR waves, from a source, with a centre frequency of 38 KHZ incident on it, its output goes low.
Lights coming from sunlight, fluorescent lamps etc. may cause disturbance to it and result in undesirable output even when the source is not transmitting IR signals. A bandpass filter, an integrator stage and an automatic gain control are used to suppress such disturbances.TSOP module has an inbuilt control circuit for amplifying the coded pulses from the IR transmitter. A signal is generated when PIN photodiode receives the signals. This input signal is received by an automatic gain control (AGC). For a range of inputs, the output is fed back to AGC in order to adjust the gain to a suitable level. The signal from AGC is passed to a band pass filter to filter undesired frequencies. After this, the signal goes to a demodulator and this demodulated output drives an npn transistor. The collector output of the transistor is obtained at pin 3 of TSOP module.Members of TSOP17xx series are sensitive to different centre frequencies of the IR spectrum. For example TSOP1738 is sensitive to 38 kHz whereasTSOP1740 to 40 kHz centre frequency.IC 7805The 78xx (sometimes L78xx, LM78xx, MC78xx...) is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost. For ICs within the family, the xx is replaced with two digits, indicating the output voltage (for example, the 7805 has a 5 volt output, while the 7812 produces 12 volts). The 78xx line are positive voltage regulators: they produce a voltage that is positive relative to a common ground. There is a related line of 79xx devices which are complementary negative voltage regulators. 78xx and 79xx ICs can be used in combination to provide positive and negative supply voltages in the same circuit.WORKING :
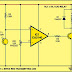
The IR signals from a remote control transmitter are sensed by the IR sensor module in the tester and its output at pin 2 goes low. This in turn switches on transistor T1 and causes LED1 to blink. At the same time, the buzzer beeps at the same rate as the incoming signals from the remote control transmitter. The pressing of different buttons on the remote control will result in different pulse rates which would change the rate at which the LED blinks.When no signal is sensed by the sensor module, output pin 2 of the sensor goes high and, as a result, transistor T1 switches off and hence LED1 and buzzer BZ1 go off. This circuit requires 5V regulated power supply which can be obtained from 9V eliminator and connected to the circuit through a jack.Capacitor C1 smoothes DC input while capacitor C2 suppresses any spikes appearing in the input supply..CIRCUIT DIAGRAM :
INFRARED IN COMMUNICATION:
IR data transmission is also employed in short-range communication among computer peripherals and personal digital assistants. These devices usually conform to standards published by IrDA, the Infrared Data Association. Remote controls and IrDA devices use infrared light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to emit infrared radiation which is focused by a plastic lens into a narrow beam. The beam is modulated, i.e. switched on and off, to encode the data. The receiver uses a silicon photodiode to convert the infrared radiation to an electric current. It responds only to the rapidly pulsing signal created by the transmitter, and filters out slowly changing infrared radiation from ambient light. Infrared communications are useful for indoor use in areas of high population density. IR does not penetrate walls and so does not interfere with other devices in adjoining rooms. Infrared is the most common way for remote controls to command appliances. Infrared remote control protocols like RC-5, SIRC, are used to communicate with infrared.Free space optical communication using infrared lasers can be a relatively inexpensive way to install a communications link in an urban area operating at up to 4 gigabit/s, compared to the cost of burying fiber optic cable.Infrared lasers are used to provide the light for optical fiber communications systems. Infrared light with a wavelength around 1,330 nm (least dispersion) or 1,550 nm (best transmission) are the best choices for standard silica fibers.IR data transmission of encoded audio versions of printed signs is being researched as an aid for visually impaired people through the RIAS (Remote Infrared Audible Signage) project.Infrared, line of sight and operating angleSince infrared (IR) remote controls use light, they require line of sight to operate the destination device. The signal can, however, be reflected by mirrors, just like any other light source.If operation is required where no line of sight is possible, for instance when controlling equipment in another room or installed in a cabinet, many brands of IR extenders are available for this on the market. Most of these have an IR receiver, picking up the IR signal and relaying it via radio waves to the remote part, which has an IR transmitter mimicking the original IR control.Infrared receivers also tend to have a more or less limited operating angle, which mainly depends on the optical characteristics of the phototransistor. However, it's easy to increase the operating angle using a matte transparent object in front of the receiver.Designed the circuit on a PCBFirst we have implemented the circuit on bread board.Then, we released the whole circuit physically to see its practical working. For this, we used a Printed Circuit Board and joined the various components on the PCB with a connecting wire using soldering it.Points to be kept in mind:
*Remote and sensor position should be adjacent to each other.*The circuit can be powered using a 9V PP3 battery.*various switch combinations can be used.*For better performance, assemble the circuit on a good PCB.APPLICATIONS:
1) Industry:Remote control is used for controlling substations, pump storage power stations and HVDC-plants. For these systems often PLC-systems working in the longwave range are used.2) MilitaryRemote controls in military usage employ jamming and countermeasures against jamming. Jammers are used to disable or sabotage the enemy's use of remote controls. The distances for military remote controls also tend to be much longer, up to intercontinental distance satellite linked remote controls used by the U.S. for their unmanned airplanes (drones) in Afghanistan, Iraq and Pakistan.Remote controls are used by insurgents in Iraq and Afghanistan to attack coalition and government troops with roadside improvised explosive devices, and terrorists in Iraq are reported in the media to use modified TV remote controls to detonate bombs.3) Space:Remote control technology is also used in space travel, for instance the Soviet Lunokhod vehicles were remote-controlled from the ground. Many space exploration rovers can be remotely controlled, though vast distance to a vehicle results in a long time delay between transmission and receipt of a command.
4) Video games:
Video game consoles had not used wireless controllers until recently, mainly because of the difficulty involved in playing the game while keeping the infrared transmitter pointed at the console. Early wireless controllers were cumbersome and when powered on alkaline batteries, lasted only a few hours before they needed replacement. Some wireless controllers were produced by third parties, in most cases using a radio link instead of infrared. Even these were very inconsistent, and in some cases, had transmission delays, making them virtually useless. The first official wireless game controller made by a first party manufacturer was the CX-42 for Atari 2600. In the current generation of gaming consoles, wireless controllers are now standard.Some wireless controllers, such as the Sony PS3 and Nintendo Wii, use Bluetooth. Others, like the Xbox 360, use proprietary wireless protocols.5) PC controlExisting infrared remote controls can be used to control PC applications. Any application that supports shortcut keys can be controlled via IR remote controls from other home devices (TV, VCR, AC). This is widely used with multimedia applications for PC based home theatre systems. For this to work, one needs a device that decodes IR remote control data signals and a PC application that communicates to this device connected to PC. Connection can be made via serial port, USB port or motherboard IrDA connector. Such devices are commercially available but can be home made using low cost micro controllers.LIRC(Linux IR Remote control) and Win-LIRC (for Windows) are software packages developed for the purpose of controlling PC using TV remote and can be also used for homebrew remote with lesser modification.ADVANTAGES:
— This circuit is simple to use and efficient.
— It can be assembled with ease.
— It is cheap and hence very economic.
— It is small in size.CONCLUSION:
With the knowledge of new techniques in ‘Electronics’ we are able to make our life more comfortable. One such application of electronics is used in “SIMPLE TV REMOTE SENSOR ”.
The same circuit finds its use in many more applications for examole in space , military , pc control.
The circuit also finds its use for switching ON and OFF any electronic circuitry. Our normal T.V remote can be used for all these purposes.
We feel that our product serves something good to this world and we like to present it before this prosperous world.
Monday, 29 July 2013
Simple Remote Control Tester
AKB. Powered by Blogger.














0 comments:
Post a Comment